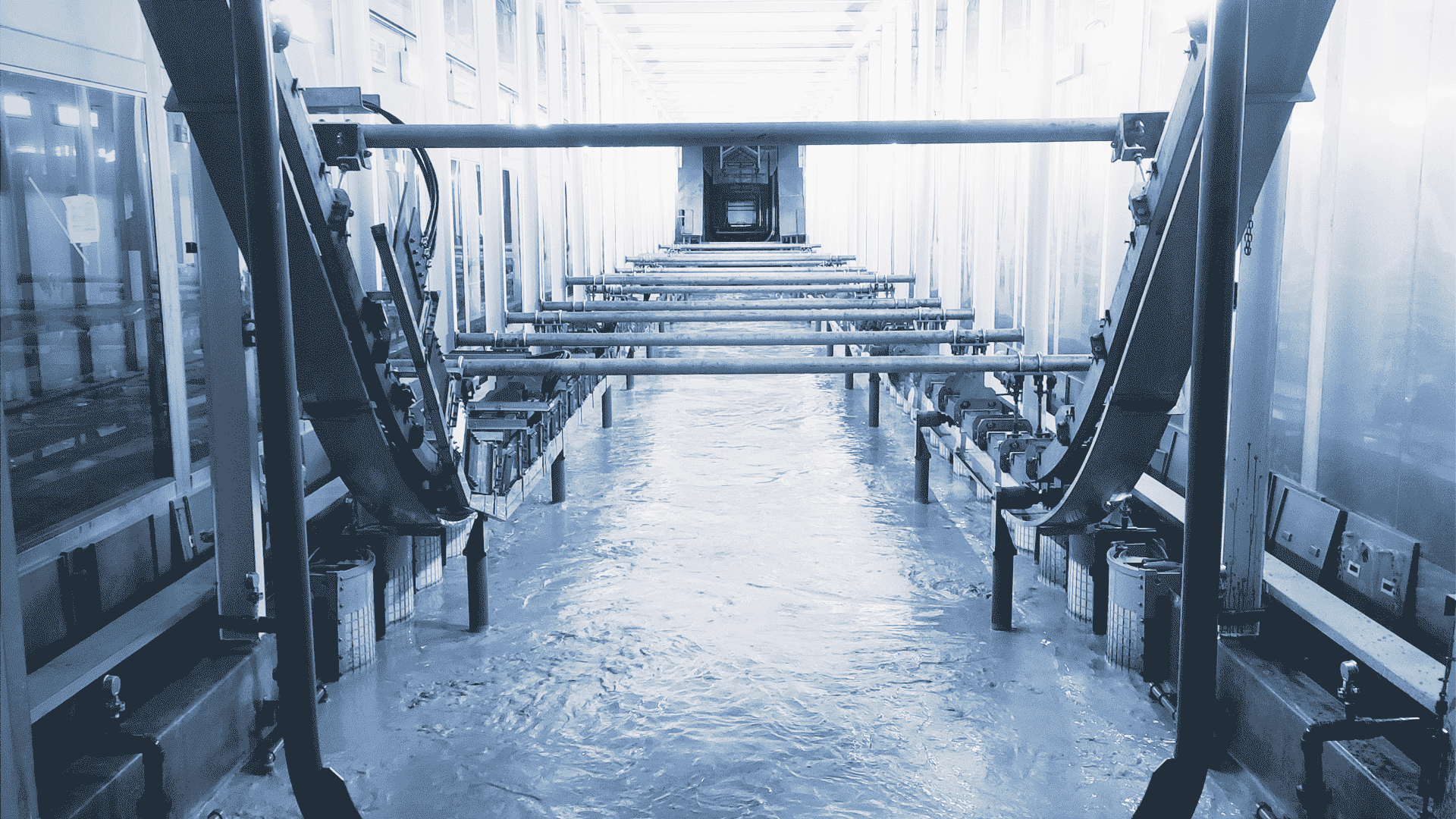
Electrophoresis coating

Electrophoresis coating technology is a kind of coating technology that deposits charged coating particles on the workpiece surface under the action of electric field. The basic principle is to immerse the workpiece into the electrophoresis tank, form an electric field between the workpiece and the electrode through the DC power supply, make the coating particles move directionally under the action of the electric field and deposit on the workpiece surface to form a uniform and dense coating. The process has the advantages of uniform coating, strong adhesion and good corrosion resistance.
Hydrogen production by water electrolysis

Electrolytic water hydrogen production is a technology that decomposes water into hydrogen and oxygen with direct current. The core equipment includes electrolytic cell and rectifier power supply. The latter converts grid or new energy alternating current into stable direct current. Electrolytic cell electrode is oxidized by anode and oxidized by cathode under the action of DC. This process is applicable to the production of green hydrogen and can be combined with renewable energy sources to achieve zero carbon emission. The electrolytic water hydrogen production power supply converts AC power into HVDC power to drive the reaction, accurately meeting the voltage and current density requirements of electrolytic cell. It is the "energy hub" for green hydrogen production. Its technical upgrading determines the efficiency and economical efficiency of hydrogen production. In the future, it will develop towards high efficiency, high adaptability and high intelligence, support large-scale hydrogen production from renewable energy sources and help global carbon neutralization.
Electric flocculation and water treatment

The electric frame condensate treatment is a water treatment technology based on the electrochemical principle. Electrolysis can aggregate suspended solids, colloid and other pollutants in water to achieve separation and purification. During electroflocculating, metal ions are dissolved from anode metals (such as aluminum and iron), and then polymeric coagulant is generated through hydrolysis and polymerization reaction.
Vacuum coating film

Vacuum coating process is a technology that deposits the material in the form of atoms or molecules to the substrate surface through physical or chemical methods in the vacuum environment to form a functional or decorative film. The core principles include physical vapor deposition (PVD, such as sputtering and evaporation) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Heating of semiconductor
The monocrystalline silicon growth process is the process of converting the polycrystalline silicon raw material into monocrystalline silicon, and the commonly used methods are CZ method (CZ method) and zone melting method (FZ method). Resistance/radio frequency heating is adopted for direct pulling method, and thermal stability is guaranteed by ± 0.5 ℃ temperature control and 0.1% accuracy power supply with millisecond level response; The zone melting rule uses high frequency induction (10-50kHz) to produce 15kW/cm? With the above power density, the double-closed loop control maintains the accuracy of 0, 2mm molten zone and drives the crystal to grow stably at 0.5-2mm/min. Both processes realize ordered arrangement of silicon atoms through precise energy control to meet the quality requirements of semiconductor crystal.
Electroplating

Electroplating is a technique in which a metal or alloy is deposited on the surface of a metal or nonmetallic substrate by electrochemical means. The core is to use electrolytic principle, immerse the workpiece as cathode into the electrolyte containing the target metal ions, and reduce the metal ions on the workpiece surface by applying direct current to form a uniform and dense coating. Plating significantly improves aesthetics, corrosion resistance, conductivity, hardness and abrasion resistance of materials.
Electrolytic metal metal
Electrolytic metal process is an industrial technology that extracts, purifies or treats metal surface from ore, compound or solution by electrolytic process. Its core is to use DC power supply to drive metal ions in electrolyte to have redox reaction on the electrode, so as to realize metal deposition (such as electroplating) or decomposition (such as electrolytic metallurgy). Electrolytic metal power supply provides continuous large current for equipment, accurately control current density, ensure stable operation, ensure uniformity of coating and improve metal purity.
Electrolytic gas

Electrolytic gas process is the process of decomposing liquid or molten electrolyte through electrolytic technology and separating gas at cathode and anode respectively. Its core principle is the redox reaction driven by DC. During electrolysis, the voltage, current density and electrolyte composition shall be accurately controlled, with high reaction selectivity and less by-products.
Smelting of rare earth

Rare earth smelting process is mainly divided into pyrometallurgy and hydrometallurgy; Rare earth metal preparation by electrolytic method (molten salt electrolysis) or metal thermal reduction method (such as calcium-thermal reduction). Pyrometallurgy includes the preparation of rare earth alloys by the silicon thermal reduction method and the high-temperature smelting technology, which is applicable to the direct extraction of rare earth metals.
Ionic membrane caustic soda

Ion membrane caustic soda process is one of the main production methods in chlor-alkali industry. Electrolysis of saturated salt water (NaCl) solution and ion exchange membrane (cation exchange membrane) divide the electrolytic cell into anode chamber and cathode chamber to realize efficient separation of chlor-alkali products.
Graphite heating

Graphite heating process is an efficient heating technology that uses the high conductivity, high temperature resistance (melting point ≥ 3650 ℃) and chemical stability of graphite materials to generate joule heat through electric current.
PCB(Printed circuit board)

PCB (printed circuit board) process refers to the technical process of laminating conductive copper foil on insulating substrate by specific technology, and forming circuit connection by etching, drilling, electroplating and other steps. Its core includes multi-layer boards, HDI (high-density interconnection) boards, flexible boards, thick copper boards and other special processes, as well as embedded technologies (such as directly embedding power chips into PCBs to achieve high-density integration).